Bicycle parking near public facilities is a major factor in the number of cyclists in a city.
Cyclists pay attention to the availability of parking spaces for their vehicles near supermarkets, educational institutions, service points and even near residential buildings. Due to the fact that not all establishments are equipped with bicycle parking, you have to fasten your bike to the nearest stationary object: a tree, handrail, road sign, fence. But this is inconvenient both for the owners of two-wheeled vehicles themselves and for pedestrians.

Clause 19 Concepts for the provision of a cycling system in Minsk, provides for the following activities to create cycling communications:
- “development of a citywide strategy for the introduction of bicycle parking lots (zoning, design and installation of new parking lots, integrated paid parking lots);
- development of new technologies for bicycle parking;
- provision of bicycle parking facilities for social infrastructure facilities;
- development of a strategy to counter theft of bicycles. "
Since the adoption of this Concept, thousands of “bicycle parking spaces” have been installed in Minsk. However, not all of them meet the requirements for them. In the MVO state: “Most of the Minsk bike parks are inconvenient. They do not allow you to properly fix the bike, to ensure its stability. This leads to the fact that cyclists do not use them, but prefer to park nearby. "
Consider the features of the existing "bicycle parking".

1. REQUIREMENTS FOR PARKING BIKES
1) requirements for their placement;
2) requirements for the main parameters (dimensions and design), including the possibility of using devices that most effectively protect parked bicycles from theft;
3) requirements for materials of structures.
2. The main parameters (dimensions and design) of "bicycle parking spaces" should provide:
1) convenience when placing a bicycle in the "bicycle parking" and removing it from there;
2) no interference with neighboring bicycles and pedestrians;
3) reliable and rigid fixation of the bicycle in the structure, which excludes the possibility of the bicycle falling to one side and the need to use a footrest for its stability;
4) the ability to "tie" the bike to the structure of the "bike parking" with the most reliable locks. "
What can protect a bike from theft? Bicycle lock. But, as experts note, “bike locks are different, and it is very important to soberly assess the level of safety that they provide:
– cable lock... The simplest and cheapest design, which consists of the actual lock (coded or with a key) and a steel cable in a protective sheath. Cable locks are very convenient: they are easy to transport, and their considerable length allows you to fix several elements of the bike, greatly complicating the task for an attacker. The main disadvantage is low strength: the locks are quite easy to open or just break, and the cable can be snipped with a tool in a couple of seconds;
– chain lock... The locking elements themselves here practically do not differ from the previous version. But to connect them, not a cable, but a chain is used. The chain is not as convenient to use as the cable, and it weighs more, especially with a considerable length. But we win in reliability: the hijacker, armed with standard cable cutters, is almost guaranteed to fold in front of the chain;
– sectional (folding) bike lock... Experts consider this design more reliable, and it is worth agreeing with them. The locking elements of the lock are connected by several hardened steel plates, and the plates themselves are joined using movable rivets. When assembled, the product fits even into a small bicycle bag, and when fixing the bicycle, it provides high reliability;
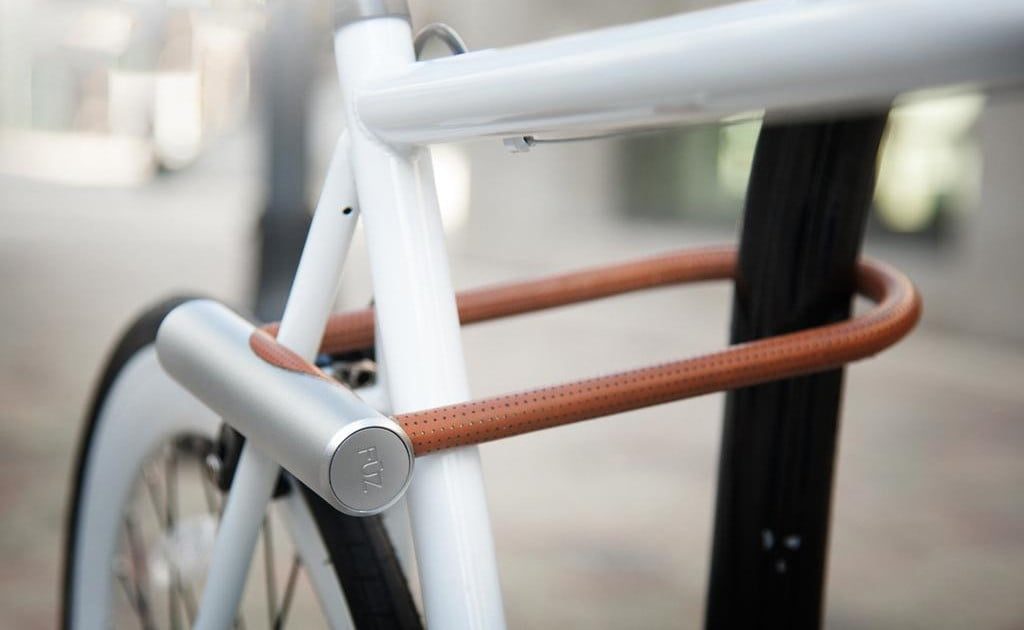
– U-shaped lock... The most reliable design that provides a good level of protection (in any case, it cannot be opened without effort). The base of the lock is a large enough hardened steel shackle, made in the shape of a U. The edges of the shackle are connected with a steel lintel to the lock, so to steal an attacker will either have to break the locking mechanism or cut a thick steel bar. The disadvantages of such locks are high cost, significant weight and by no means compact size. "
One can argue with the fact that U-shaped locks have "significant weight and are by no means compact in size" - their dimensions can be estimated in the photo below.
A bicycle lock with a cable of any production can be eaten with a special hand tool, incl. ordinary side cutters (nippers), in a short time. The only way to prevent theft of a bicycle when using locks is a hardened chain with a rod thickness of 6 mm or more or a U-shaped lock with a massive hardened bow. It is possible to saw through such chains and shackles only with a "grinder", which is difficult to do at a "bicycle parking" in the city. It should be noted that, despite the advertising, hot ropes do not exist, otherwise they would have burst when bent. Hence the conclusion: the best option for protecting a bicycle when parking it is a U-shaped lock with a massive hardened bow.

The only document that establishes the requirements for the basic parameters of "bicycle parking spaces" is TKP 45-3.03-227 ... In sub. 5.5.6 of which it says: "For temporary storage of bicycles, parking areas with dimensions of 2.0 × 0.6 m for one bicycle, separated by racks (brackets) 0.75 high and 1.6 m long, should be provided." From which it follows that "bicycle parking spaces" are:
1) territory measuring 2.0 × 0.6 m per bike;
2) separated by uprights (brackets) 0.75 m high and 1.6 m long (which is clearly redundant).
Does at least one “bicycle parking space” in Minsk meet these requirements?
3. The legislation does not contain requirements for the construction materials of "bicycle parking", as a result of which it is often possible to observe unreliable and rusty structures.
It should be noted that in many foreign countries detailed documents have been developed containing requirements for "bicycle parking spaces".
2. MBO RECOMMENDATIONS FOR BIKE PARKING SPACES
Recommendations for bike parking locations
1. Visibility. The bike rack must be clearly visible from a distance. The easier it is to find it, the more likely it will be in demand. Signs and signs on the availability of such a parking lot and its location can serve as additional clues for cyclists.
2. Distance to parking. The best location is near the entrance to the building (structure) at a distance of no more than 15 meters.
3. Availability. Cycle parking must be easy and unimpeded access. The approach to the parking lot should not intersect with the movement of pedestrians and motor vehicles or be obstructed by other objects (flower beds, benches, lighting poles, etc.).
4. Security. Bicycle parking should not block emergency exits from buildings, block sewer hatches, ramps, stairs and approaches to them. Placement near window openings should also be avoided. Bicycle parking should not obstruct the view at intersections and pedestrian crossings. Do not place stands along roads closer than 0.8 m from the edge of the carriageway.
5. Bicycle parking at an angle of 45 ° saves space on the sidewalk. It also has a number of advantages:
- less likely to get confused by the handlebars of bicycles;
- less space is needed to move the bike out of the parking lot.
Recommendations for the construction of "bike parking"
1. The bike must stand firmly on a horizontal platform, must not roll over to the side or roll forward / backward. Both wheels should be in contact with the sidewalk, neither should be lifted by the curb or parking structures that would compromise the stability of the bike.
2. One of the best designs for bicycle parking is U-shaped racks (or in the form of an inverted U), which is characterized by the following:
1) low cost, ease of installation and good appearance, which fits into the street environment;
2) two bicycles can be parked at one such rack, which saves construction material and allows efficient use of the “bike parking” area;
3) the shape of such a rack allows you to fix the bike with reliable U-locks in two places (frame and wheel). At the same time, to be able to fix the bicycle frame to the rack, the distance from the rack to the wall of a building (structure) or other object (for example, a tree) should be at least 600 mm, and the distance between adjacent racks should be 750-850 mm.
3. Structures holding the bike by one wheel should be avoided. Such structures also include U-shaped racks installed close to the wall of a building (structure), as a result of which the bicycle frame cannot be "leaned" against the rack. The bike must be “fastened” to the rack by the frame for the following reasons:
1) if only the wheel is “tied” to the structure, the rest of the bike can be stolen. In modern models, the wheels are attached to the fork with an eccentric (clamp) and they can be easily separated from the fork without the use of tools in a minute;
2) when the bike falls (for example, someone touches it), the load from the sideways tilting bike is transmitted through the fork to the front wheel fixed in the structure, creating a torque, and taking into account the weight of the bike, about 15 kg. and a significant leverage of the application of force, the eversion of the wheel and its damage (bending of the rim) may occur;
3) such structures can damage the brake disc or scratch the bicycle fork;
4) when designing such a structure, one should take into account the width of the bicycle wheel, which varies in the range from 23 to 80 mm. Consequently, parking for one type of bike may become unusable for another.
Requirements for materials of construction of "bicycle parking"
1. The stand must be made of materials strong enough to prevent thieves from breaking it with ordinary hand tools. Bicycle stands must be securely fastened.
2. For the durability of the racks, it is necessary to choose high-quality materials and types of coverage.
1) black metal is cheap, but short-lived and requires maintenance. Most often in Belarus, bicycle parking is made of black steel. Due to the specifics of the use of parking lots, after a year, their structures can begin to rust. To prevent this from happening, you should use a zinc-containing primer and a high-quality multilayer powder coating;
2) galvanized steel - with good quality it will withstand a five-year period. Galvanized steel structures will not rust even if the protective layer of paint or polymer is damaged. They can be used for 5 years without cosmetic repairs. But it is important that the galvanizing is done with high quality. With cold galvanizing, the zinc layer burns out at the welding points, which subsequently leads to the appearance of rust;
3) stainless steel - just put it on and forget it. It is the most reliable and durable material that does not require painting and looks great. Its only drawback - its high cost - is compensated by its almost unlimited service life.
3. EXISTING BIKE PARKING AREAS IN MINSK
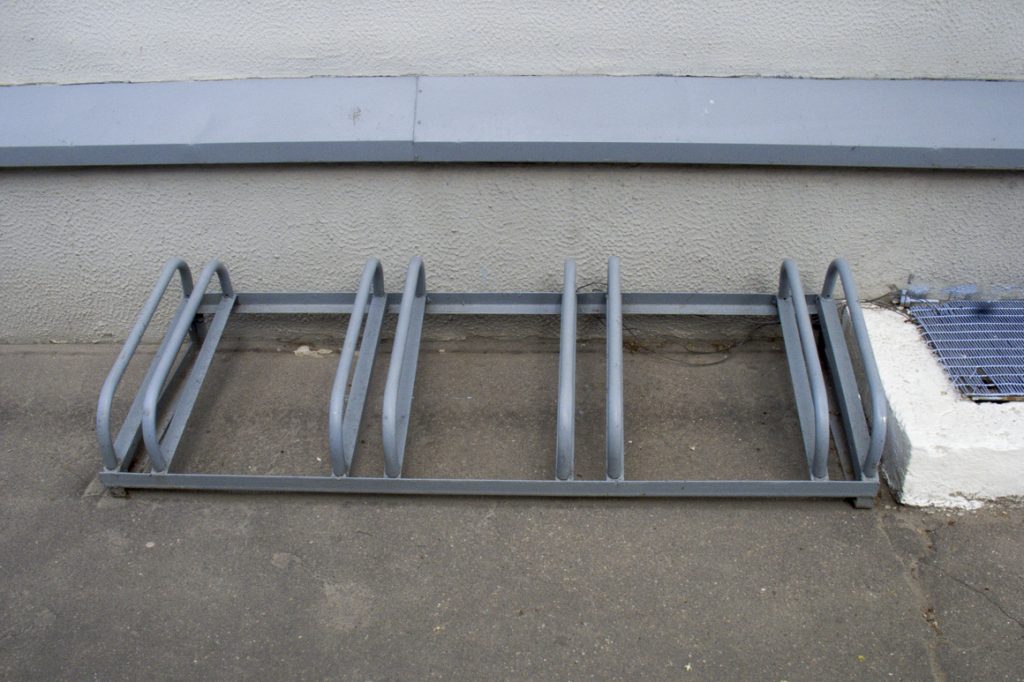
A rare case of constructively correct "bike parking"
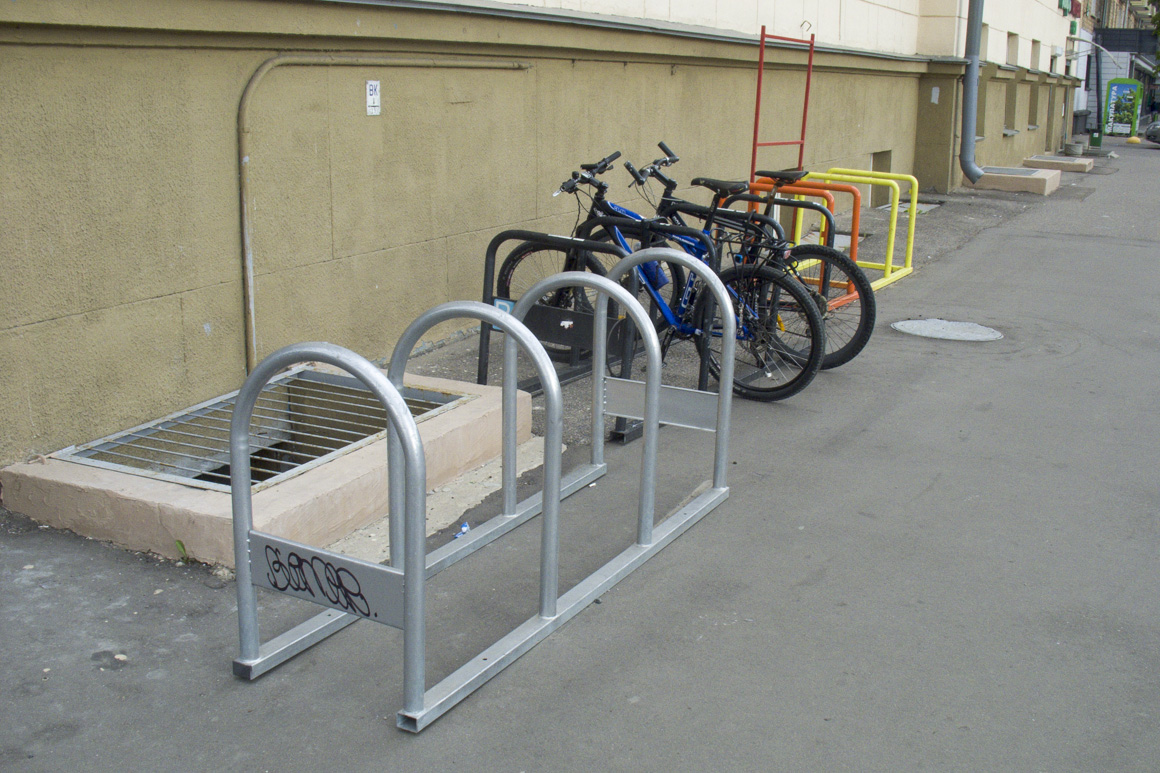
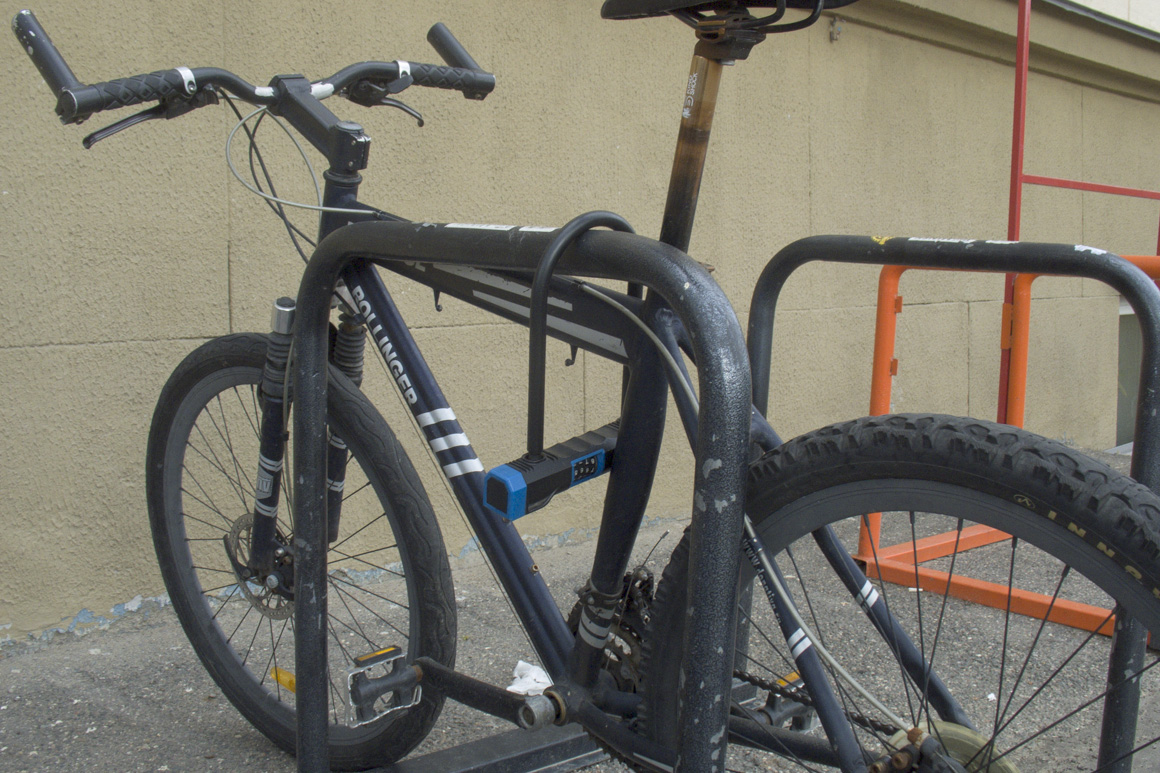
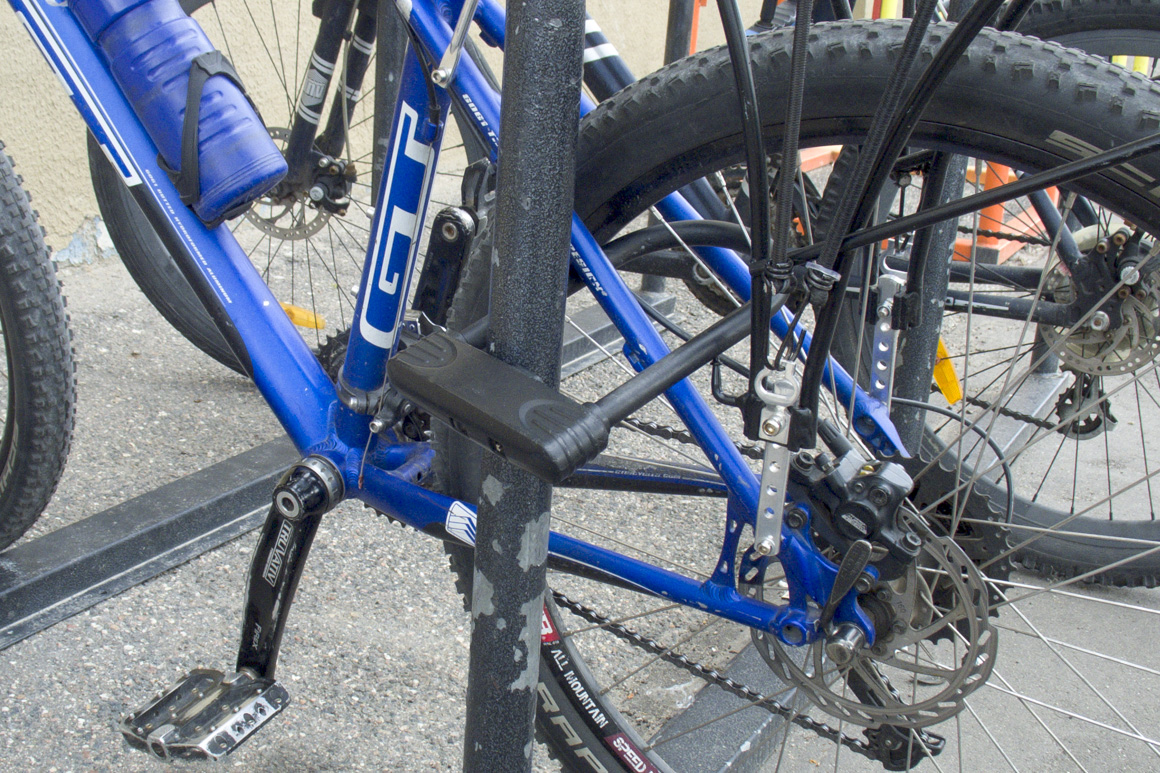
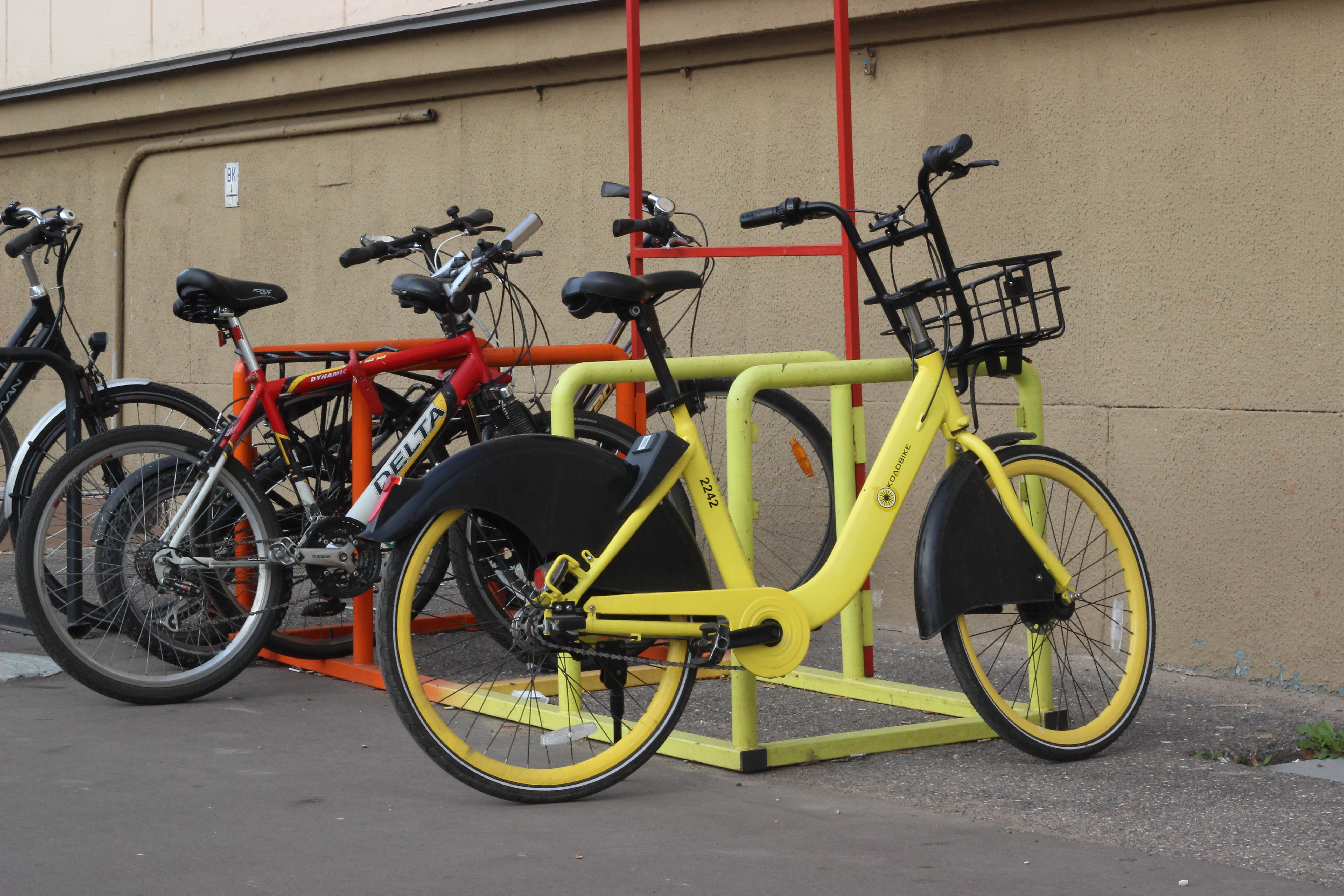




A series of U-shaped brackets installed at a sufficient distance both from the wall of the building (space for the front wheel is provided) and from each other. In such a “bicycle parking”, you can firmly “fasten” not only the frame, but also two wheels of any bicycle to a metal bracket using a reliable U-shaped lock.
Almost correct parking
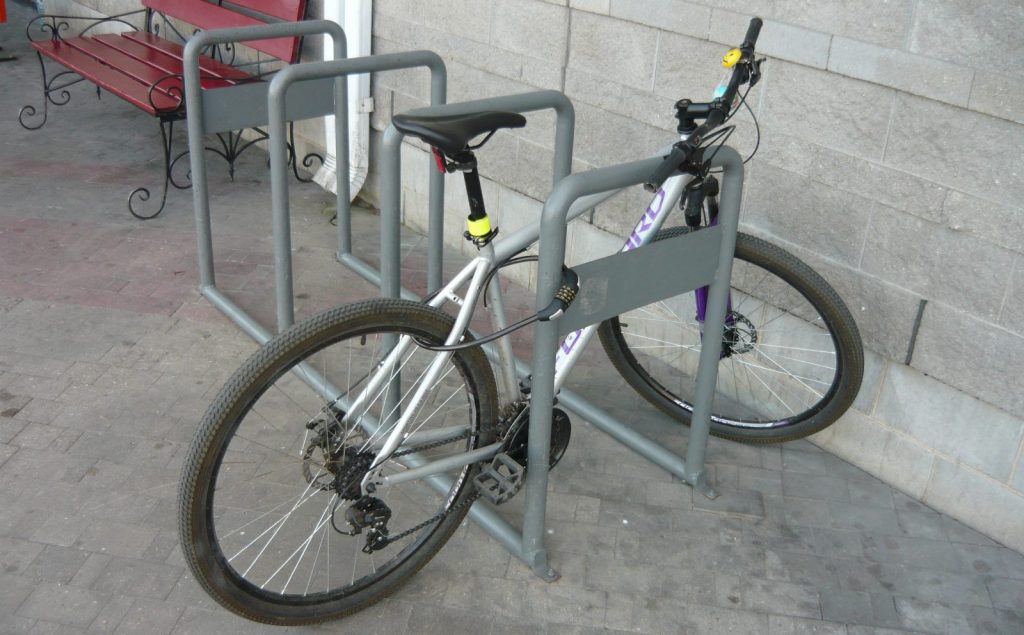
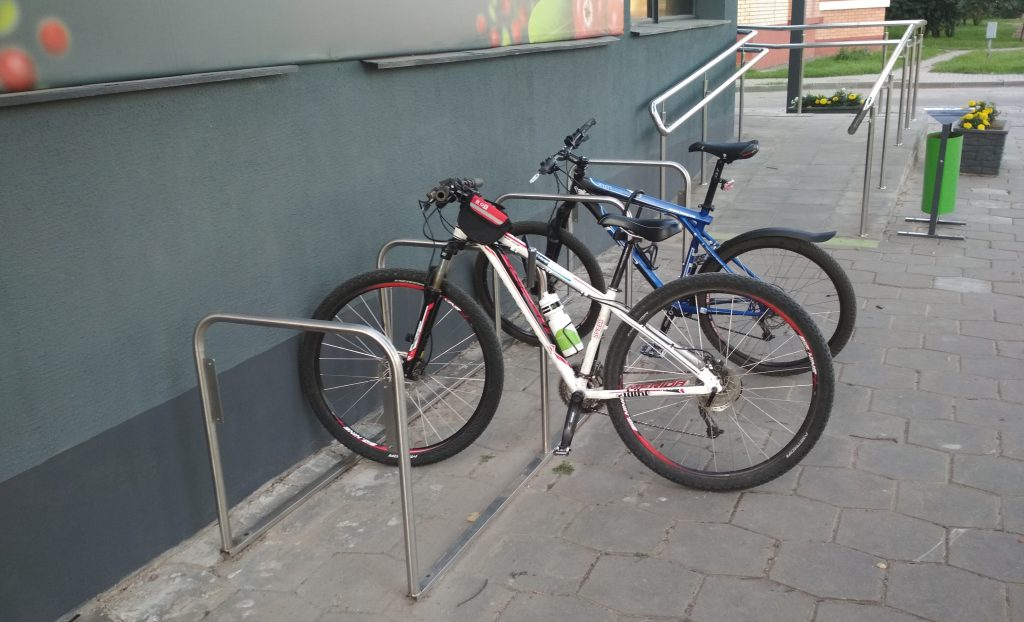


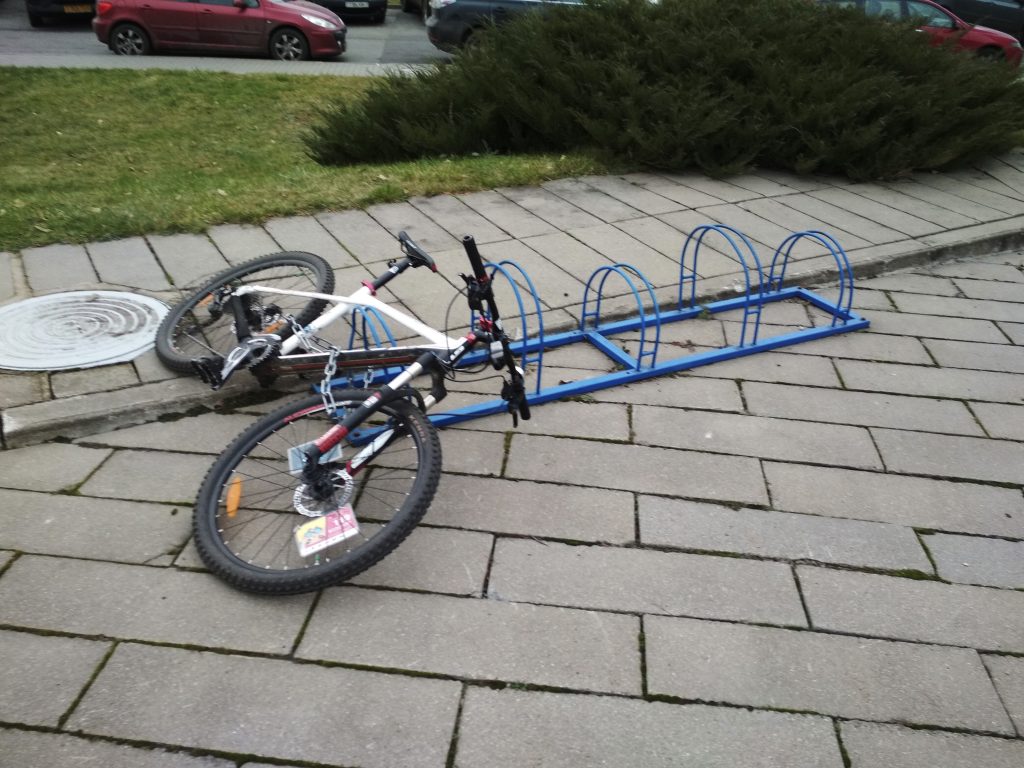
The same row of U-shaped brackets installed at a sufficient distance from each other, but close to a wall or a tree, as a result of which there is no room for the front wheel. At such a “bicycle parking”, only the bicycle frame and one wheel can be “fastened” to the metal bracket firmly and securely with the help of a U-shaped lock, while the second wheel will “protrude” beyond the “bicycle parking”.
Small arc design
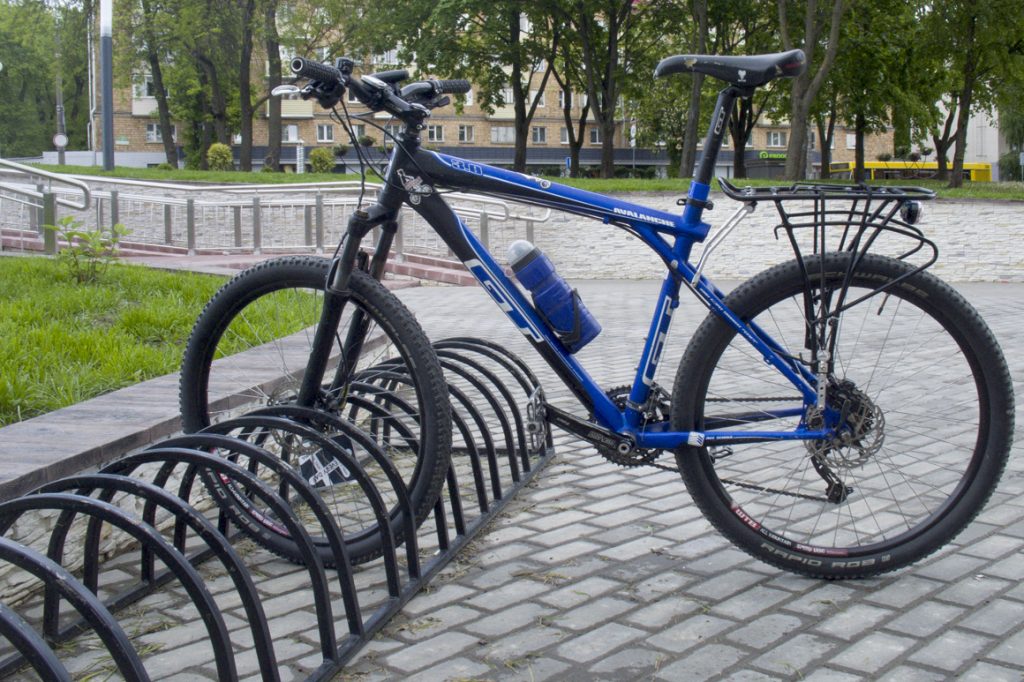
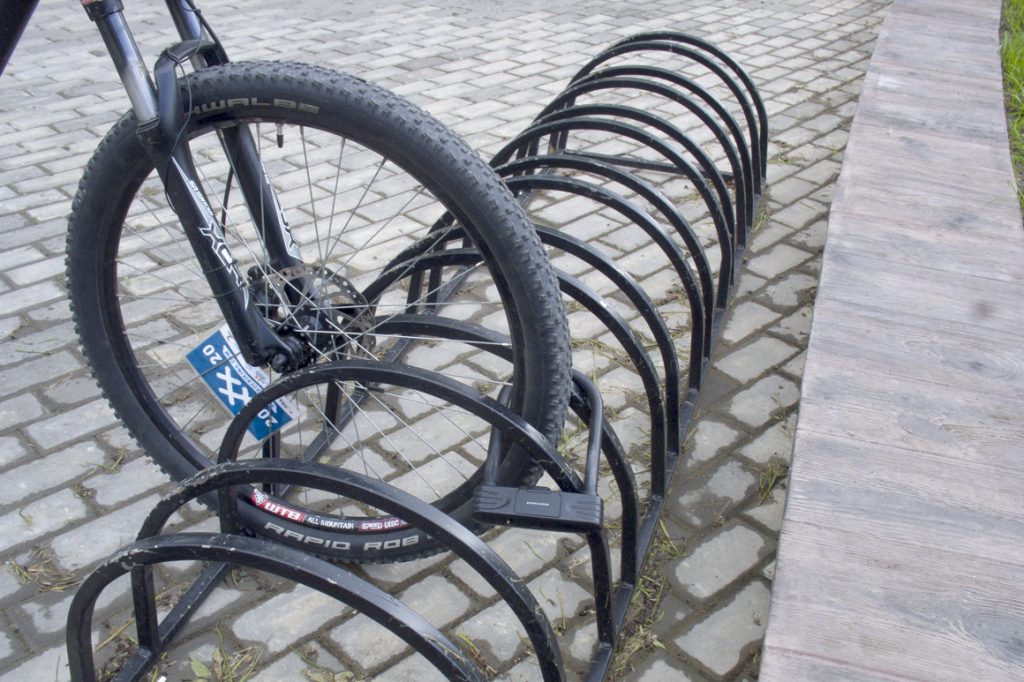
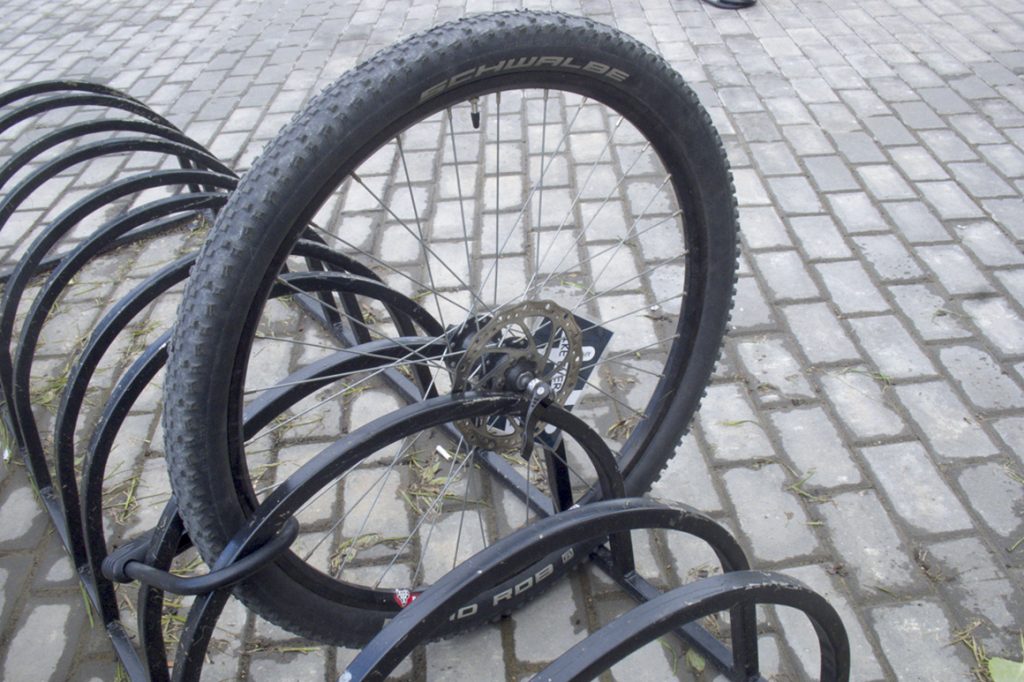
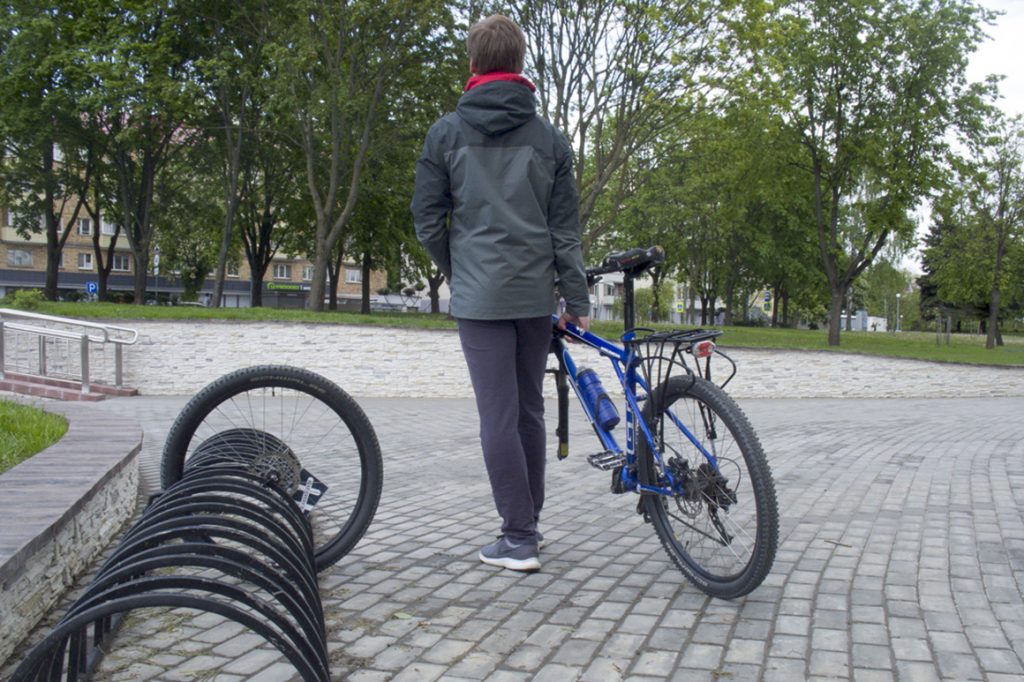





The design consists of groups of closely spaced arcs designed to fit the wheel between them. These groups of arcs are placed at some distance from each other so that adjacent bicycles do not interfere with each other.
The wheels of not all bicycles will fit between closely spaced arcs. And for those that fit, there is a real danger of bending the brake disc or scratching the bike fork.
If you insert a wheel between groups of closely spaced arcs (between wide-standing arches), then the bicycle will be unstable. Its front wheel can be "tied" to the arches, incl. and a U-shaped lock, but in this case there is a threat to bend the wheel rim when the bike falls from the push, as well as the threat of theft of the bike by separating the fork from the wheel (see photo).
It is no coincidence that such "bike racks" are not popular with cyclists who prefer to park their bicycles next to them (see the last photo).
Next "bike parking"
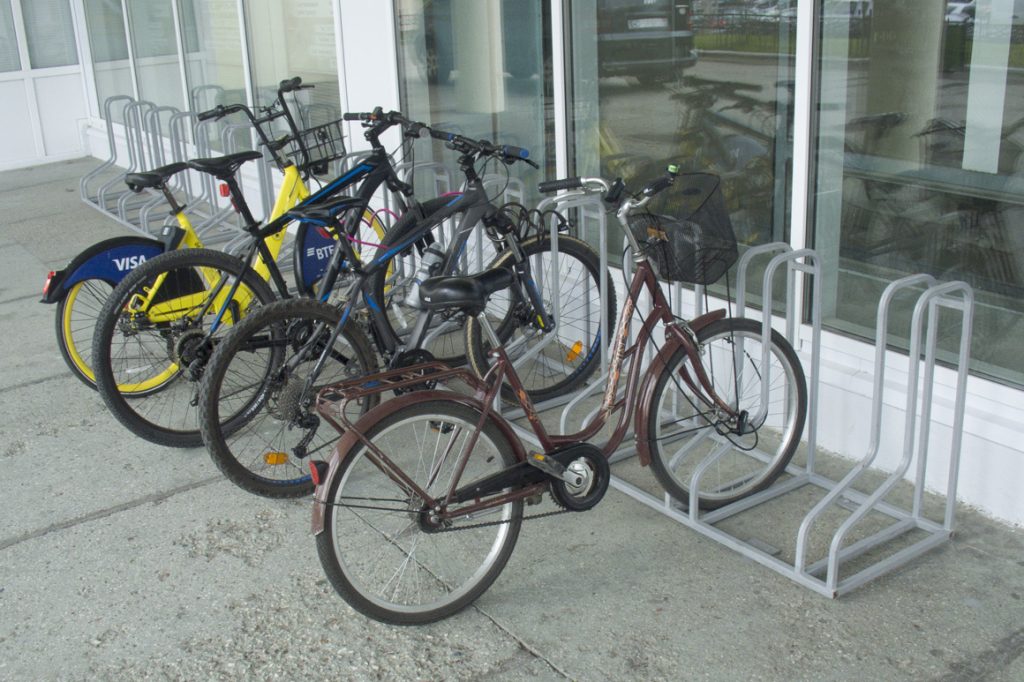
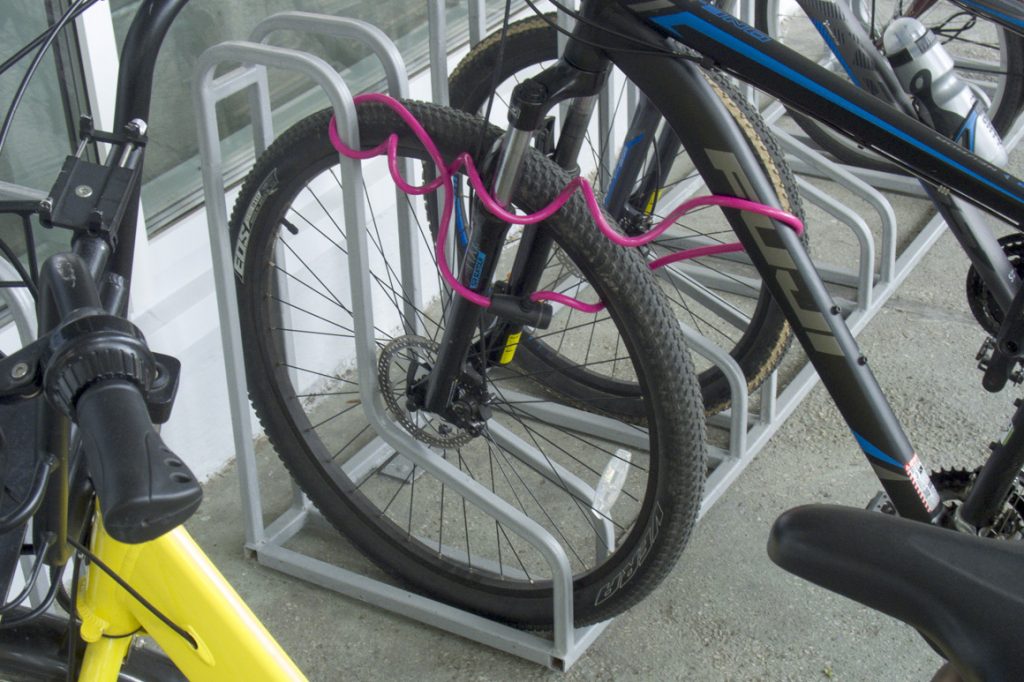


At such a "bicycle parking" the same problems arise as at the previous one. However, it is sometimes possible to "tie" the frame to this structure with a cable lock, but not with a U-lock.
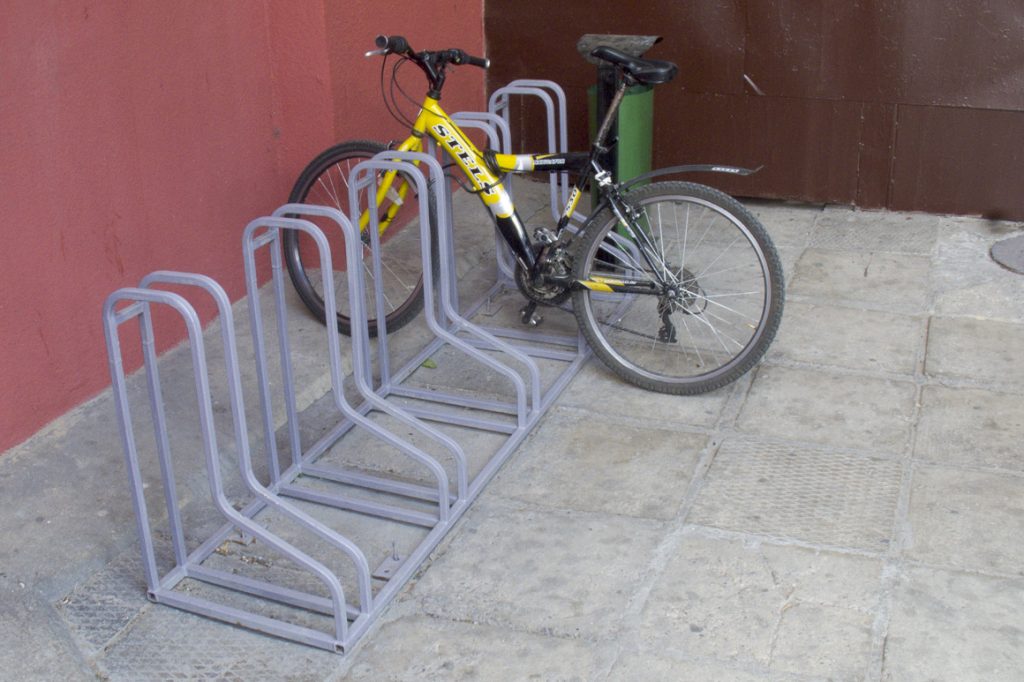

In the general case, such a bicycle parking design provides for fastening a bicycle to a wheel and is usually installed close to a building (structure). The photo above is interesting precisely because of the unusual way of parking a bicycle, which is not typical for this type of parking. Often, resourceful cyclists try to move such a structure away from the wall so that it becomes possible to attach a bicycle not only to the front wheel, but also to the frame. A more comfortable and safer way, so to speak. Also, very often, the wheel (fork) of the bicycle simply does not fit between the provided arches of such bicycle parking lots. Perhaps this is the reason for choosing a different parking method for the yellow bicycle, more comfortable and stable. However, with such an arrangement and use of a bicycle parking, most of its constructive functionality is wasted. This is expressed in the fact that with such a parking lot of the bike, as in the photo, you cannot put another one next to it - there is not enough space. Unlike, for example, a U-shaped product, in which parking is possible on both sides. At the same time, almost half of the materials will be spent on the manufacture of the latter.
Small triangular design
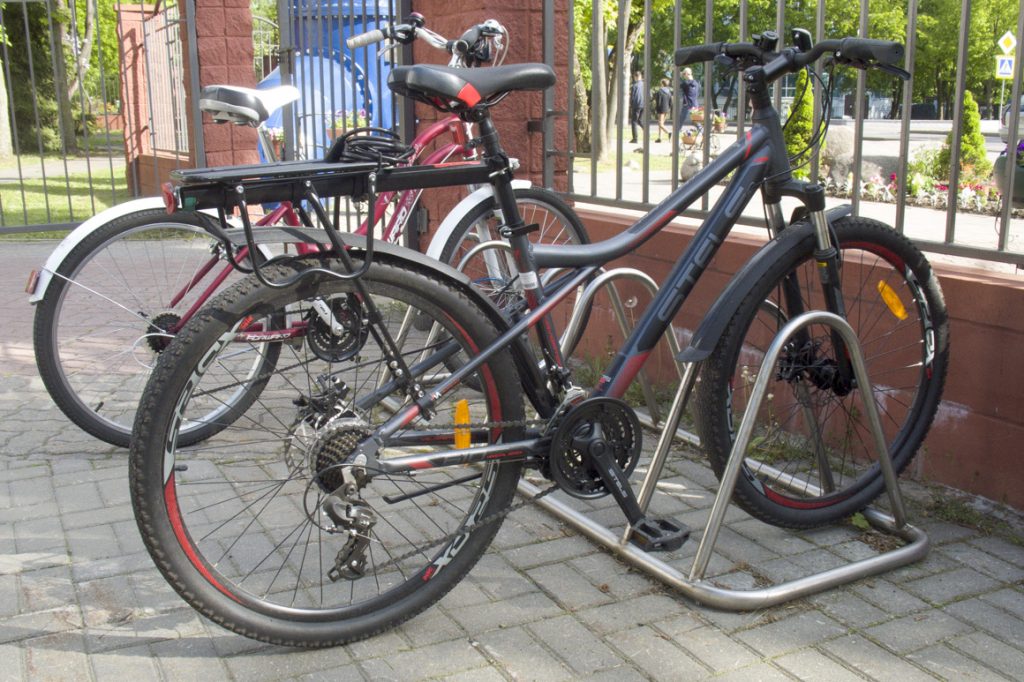
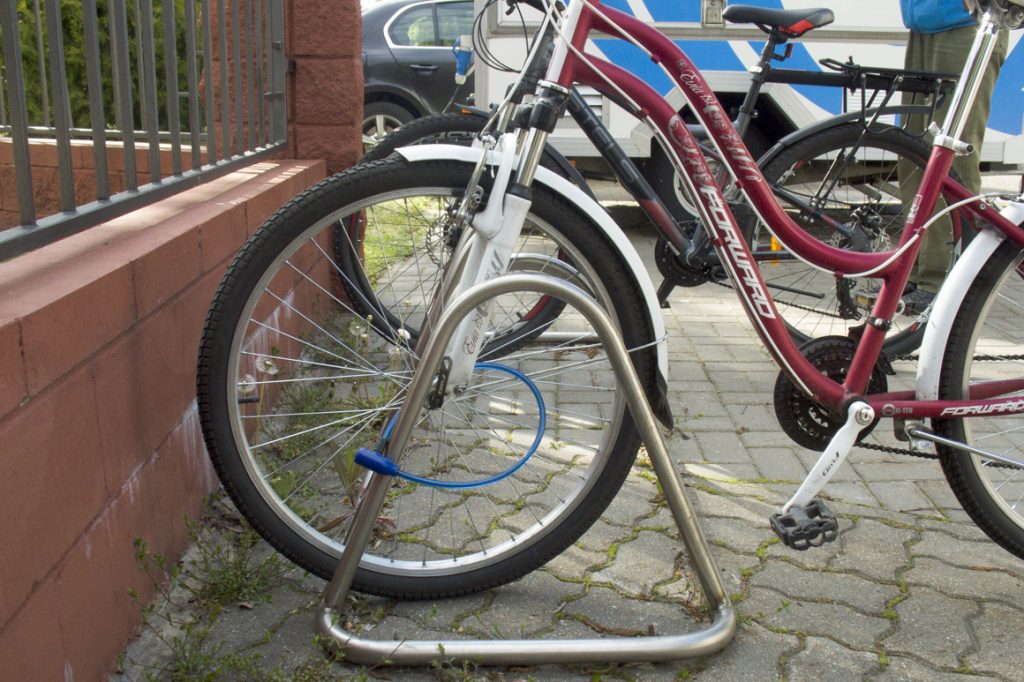


The problems are the same.
Large arc construction
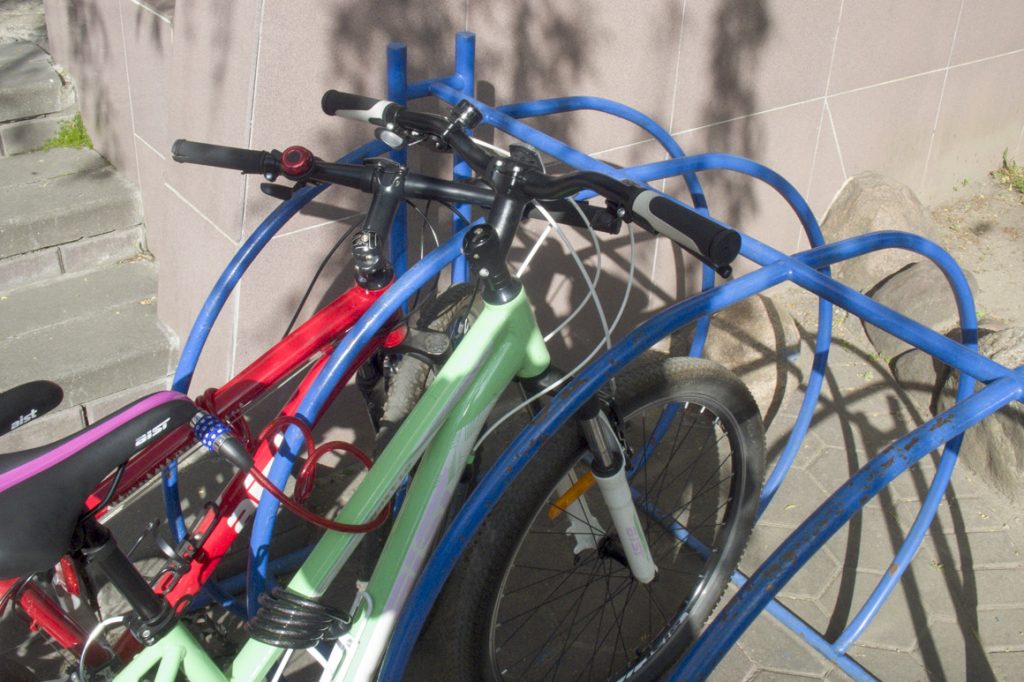
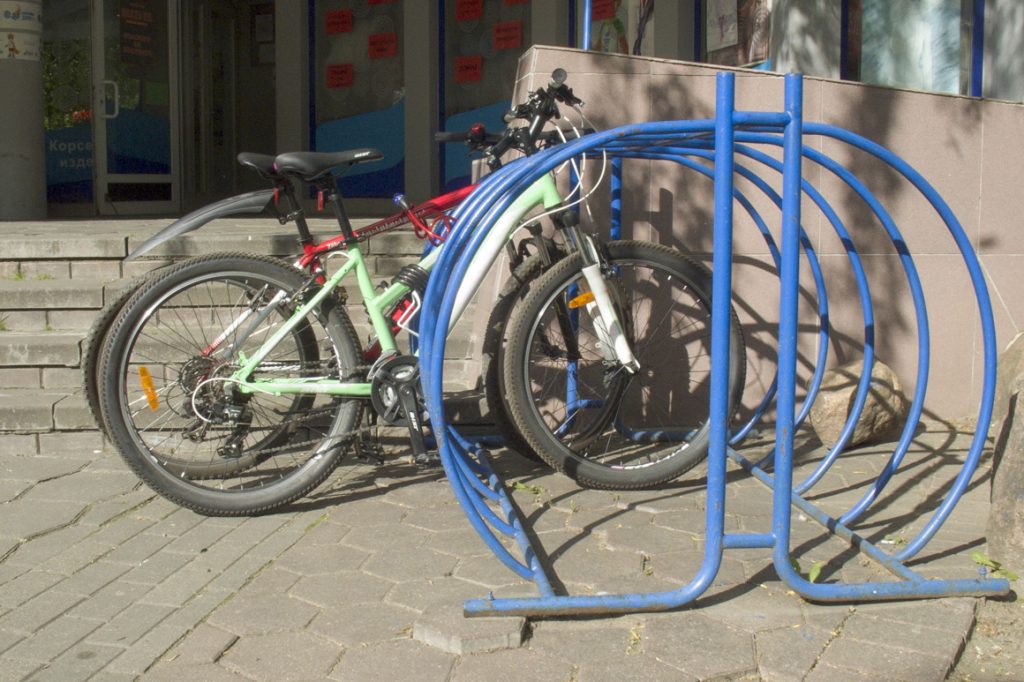
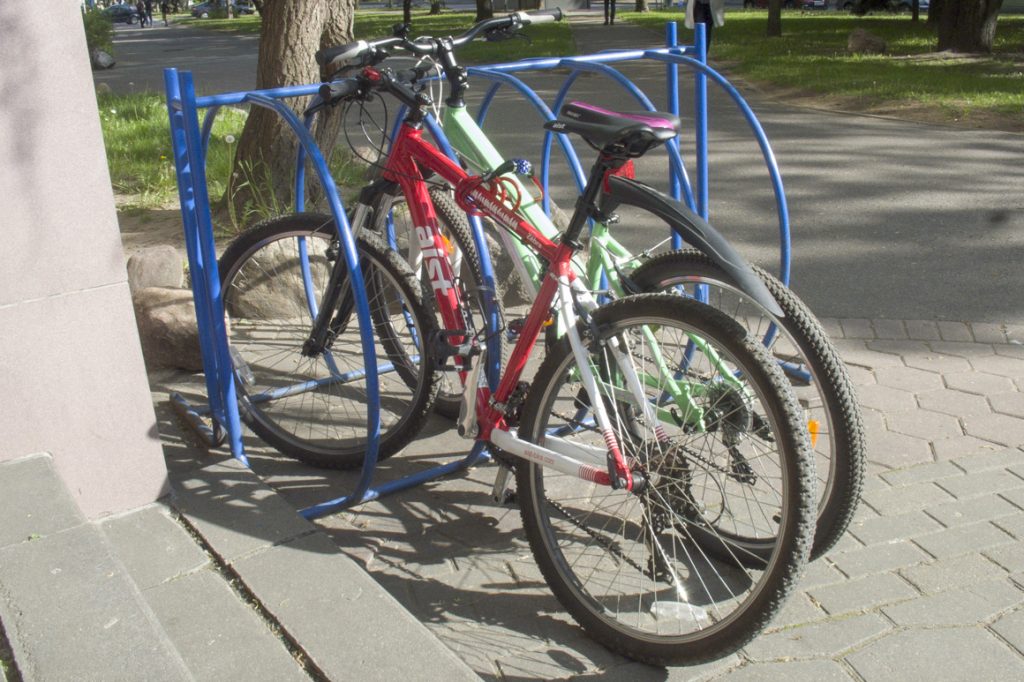


To such arcs it is possible to "tie" the frame and one wheel of some bicycles with the help of a U-shaped lock. Although, the owners of these bicycles simply "tied" their frames to each other with a cable lock.
Small triangular design
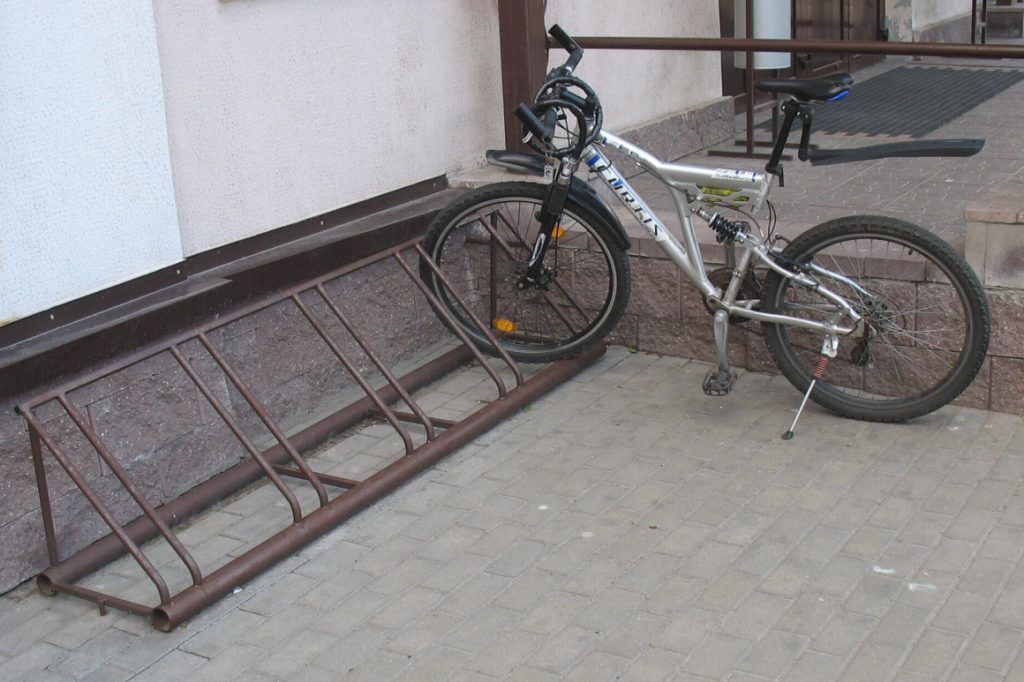

Rusty construction. The wheels of not all bicycles will fit between closely spaced "rods". And for those that fit, there is a real danger of bending the brake disc or scratching the bike fork. If you insert a wheel between widely spaced "rods", the bike will be unstable. So, to give stability, the owner of this bike used a footrest.
Unusual design
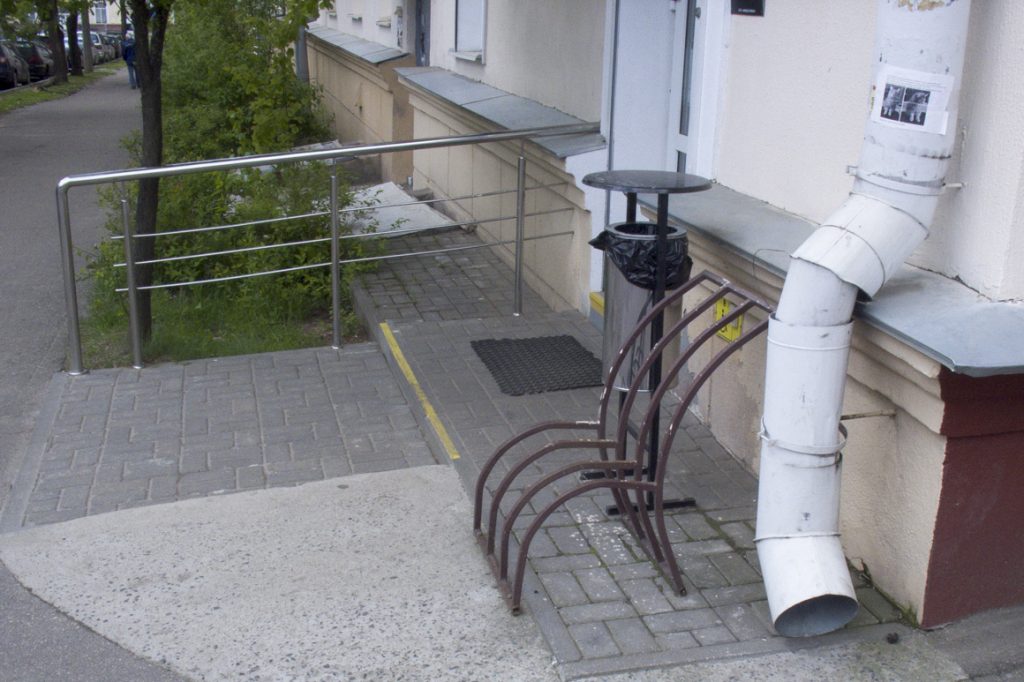

This rusty design has room for the front wheel and there is no chance of a U-lock on the frame. Isn't it easier to "tie" the bike to a nearby handrail? Both the structure itself and the railings are located near the entrance to the public premises. Will fire safety rules be violated with such parking? About this question the representative of the Ministry of Emergency Situations explained: “All buildings have escape routes, and if a bike blocks them, it violates fire safety rules. It is very easy to determine if a bicycle is interfering with someone. Imagine a crowd of people running out of a building: if the same number of people can get out through the escape route with a bicycle as without a bicycle, then everything is in order. Most likely, if the bike is physically on the porch or on the stairs, then it interferes with the evacuation. And if it is on the outside of the stairs and is fastened to the railing, then it does not interfere. "
Another option for "bicycle parking"
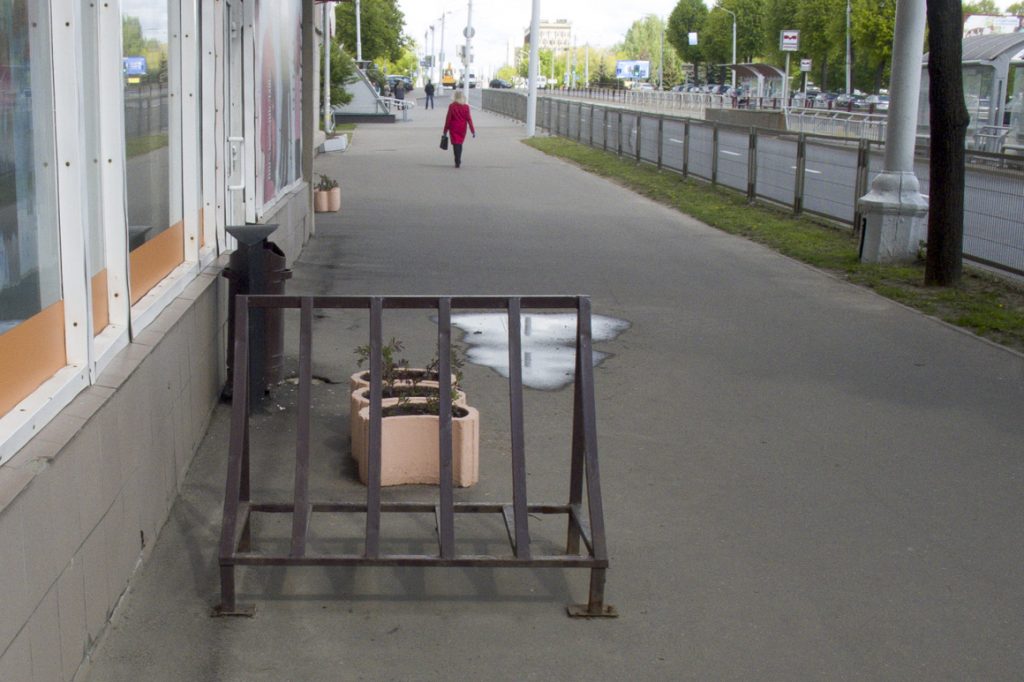
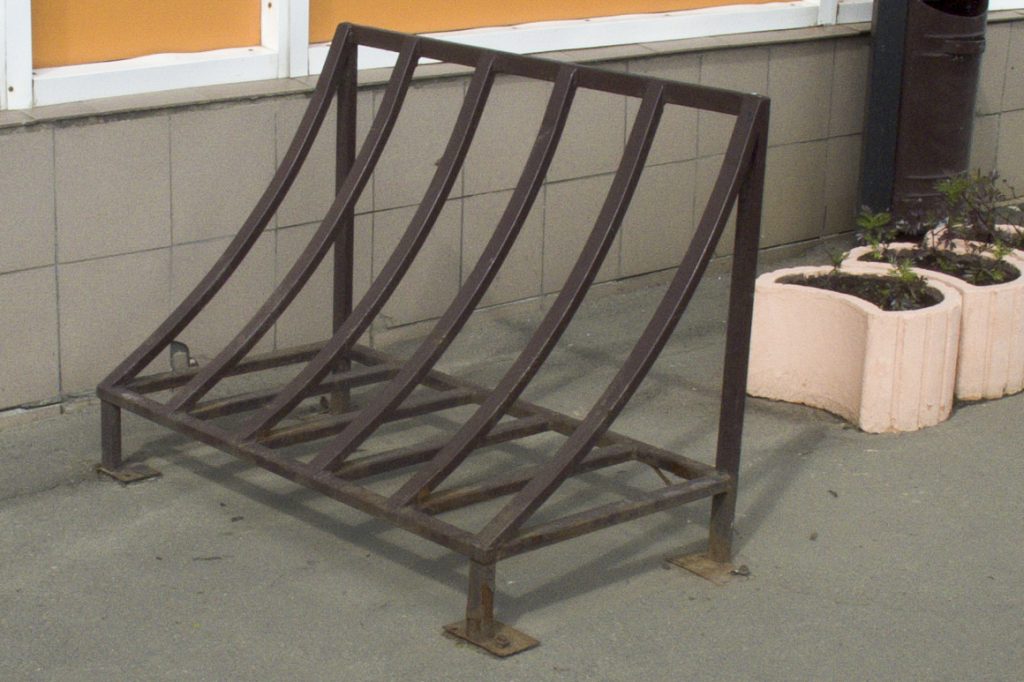


It seems to be nothing out of the ordinary - another rusty triangular structure. But bicycles parked on it are not located across the sidewalk, creating an obstacle for pedestrians, but along the sidewalk. Relevant for narrow sidewalks.
Another variant of the triangular design
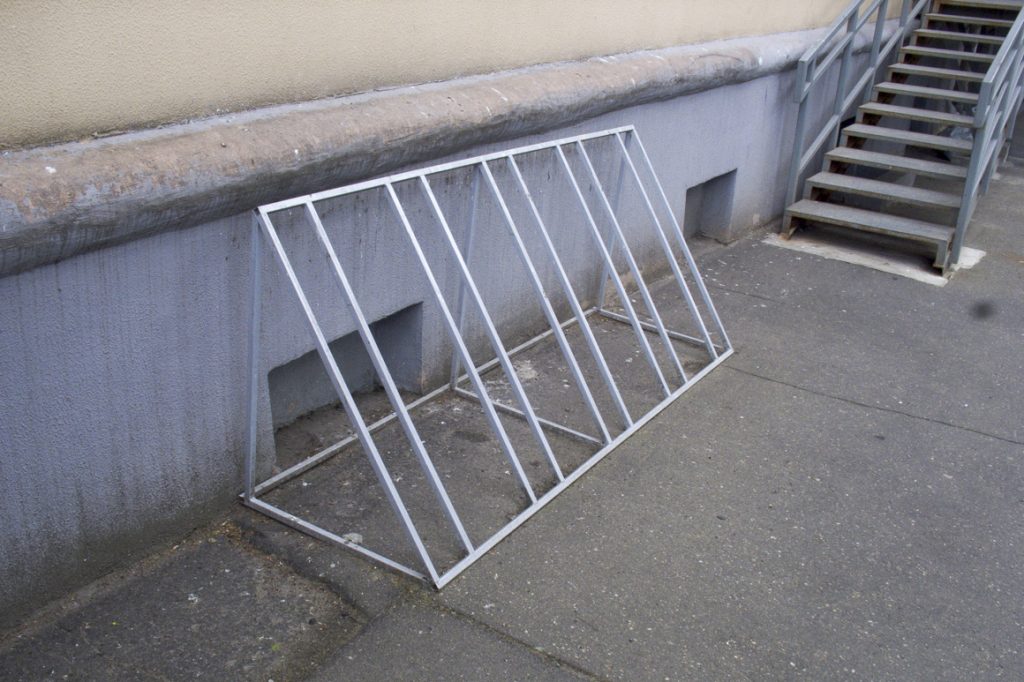

The construction of welded and painted metal rods is cheap and cheerful, but not convenient and not practical.
The following construction is triangular
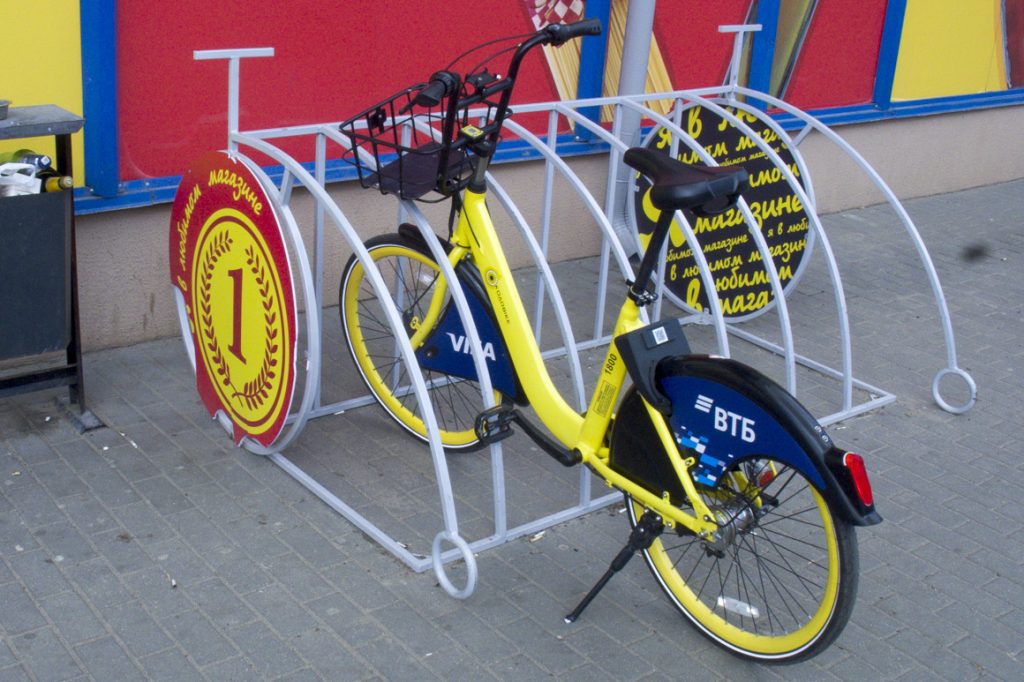

A footrest is used to stabilize the parked bike. There is a chance to "tie" at least some bicycles to the frame with a U-lock.
Trap-type low struts construction
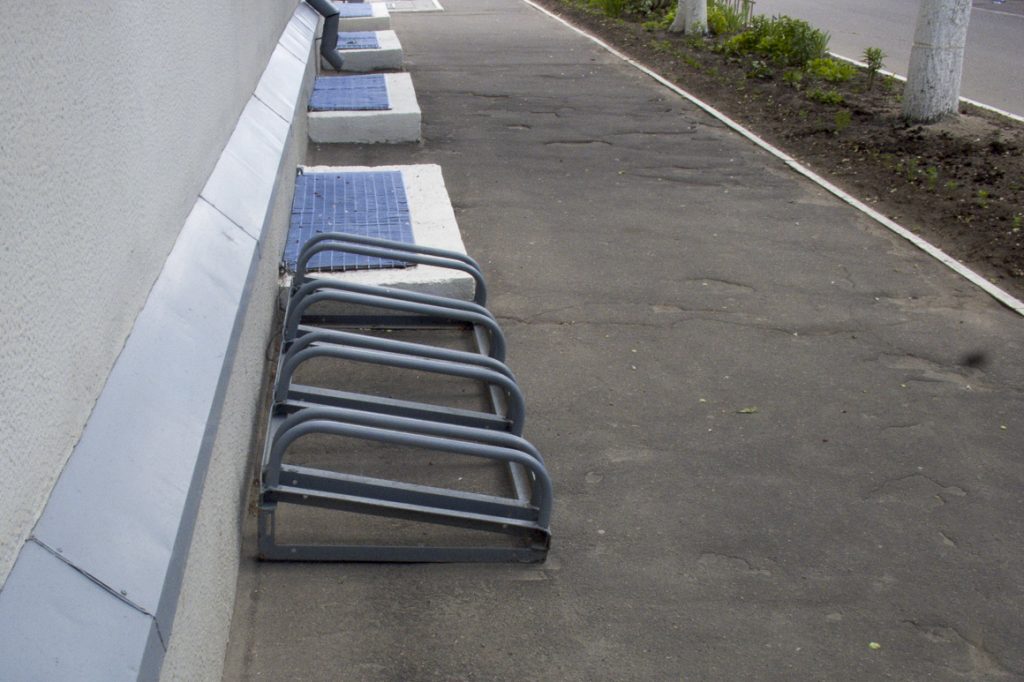


There is no need to talk about the stability of a bicycle parked on such a structure ... Moreover, this structure is located on a narrow sidewalk and parked bicycles will interfere with pedestrians.
With regard to similar structures the representative of the MBO notes: “Geta is a sapradnaya icon for a villain ... Mala tago, INTO the great parks, the mighty pagnus of the tarmazny dysk, or the padrapats lku velasipeda, Duc and the bypassed pakinuts here their two-wheeled transport is practical. At the current velasіpedahs, they often pick an eccentryk, as the cola is easy to use. Navat skarystaўshysya lock, yes veragodnasts, INTO the villain adtsyagnne the lever of the eccentric and the adluts "intact" transport hell "legs". And ў getai flock of skarystatsa “akhovay” is possible only praz kola, not often in the hands of chalavek sydze with kulgavy on adnu apora velasipedam ”.
U-pillars construction
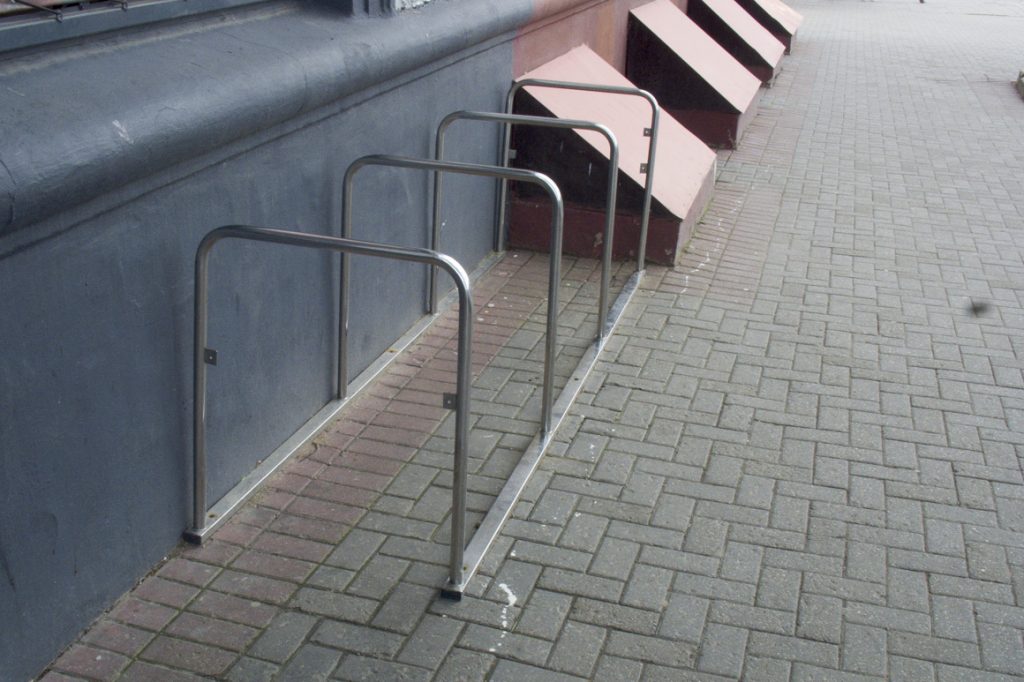

Everything would be fine if the structure was not installed directly next to the wall of the building. The lack of space for the front wheel prevents the bike from being tied to the rack using U-shaped locks for the frame and two wheels. At the same time, if you move the structure away from the wall, then the parked bicycles will interfere even more with pedestrians ...
Best example
Nevertheless, we managed to find a sample of the correct bicycle parking in the city. Moreover, it is ideal for all the key indicators that we noted earlier: location, design or shape, materials of manufacture. Oddly enough, a regular grocery store installed such a bicycle parking for its cycling customers. After all, not even every administrative institution in Minsk will be able to boast of having an approximate parking space for a bicycle.
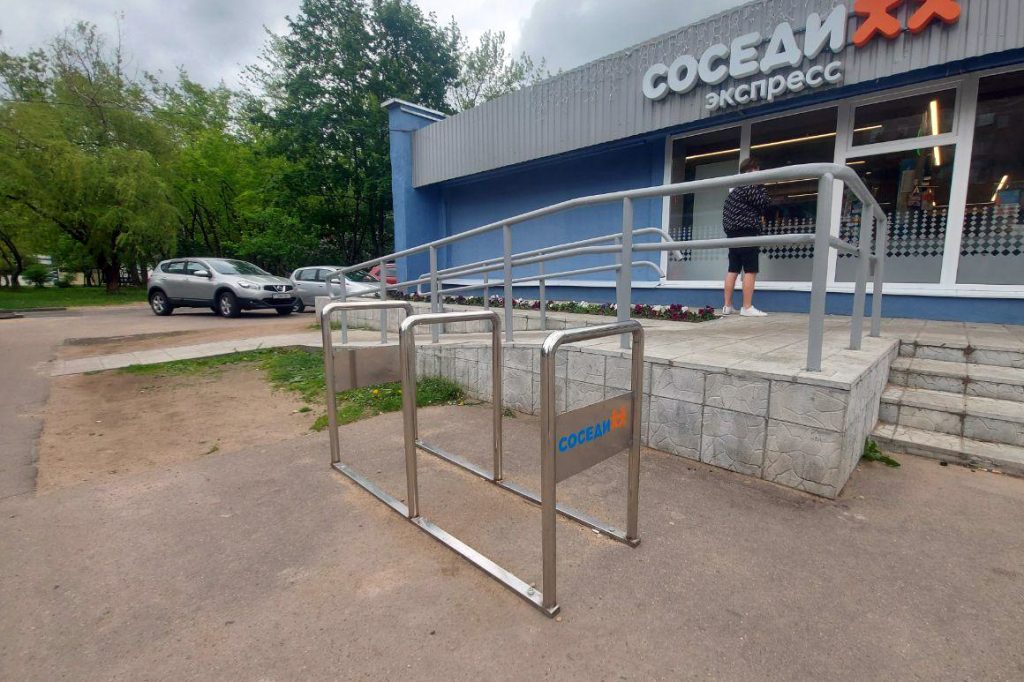

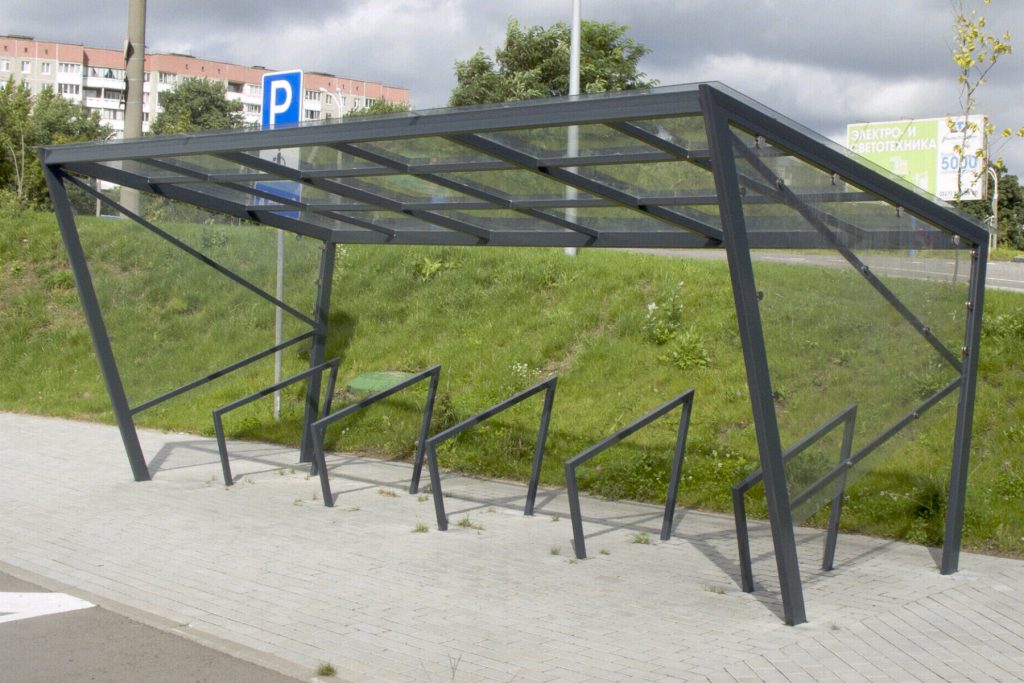
Bonus
Bicycle parking with a canopy will help protect your bike not only from theft, but also from bad weather. There are several such bike parks in Minsk. One of the highest quality is located near the business center outside the Moscow Ring Road. I would like such places for parking lots bicycles appeared in transport hubs - at train stations and near metro stations.









